NANOPARTICLE THERANOSTICS .
The development of nanomaterials as multifunctional targeted therapeutic and diagnostic (theranostic) imaging agents has become increasingly important in recent years, potentially providing powerful, sensitised means of co-localising physiological/disease status and anatomy. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a powerful non-invasive medical technique which becomes considerably more potent when contrast agents are applied. Nanoparticle design in the group is broad, spanning a range of scaffolds including inorganic (silica and iron oxide nanoparticles), inorganic-organic hybrid (polymer grafted silica nanoparticles), and purely organic (polymer micelle) imaging agents. Notably, these are capable of reporting on their local biochemical environment through a stimuli-triggered (e.g. pH) ‘on/off’ switching response, enabling potent disease-specific reporting.
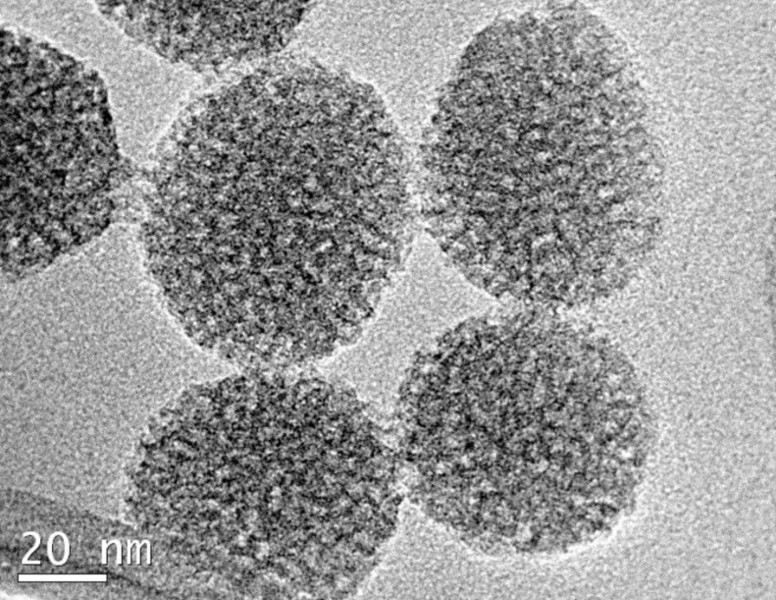
The group design and fabricate a broad range of responsive inorganic, organic and hybrid paramagnetic and super paramagnetic nanoparticles that generate high and switchable image contrast.
A major focus with many of these has been both controlling water (its access and diffusion characteristics) and molecular rotational characteristics.





EXAMPLES .
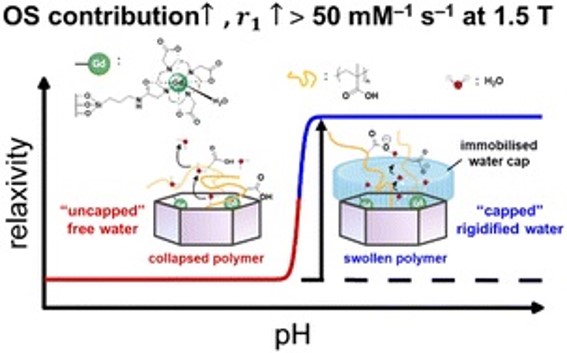
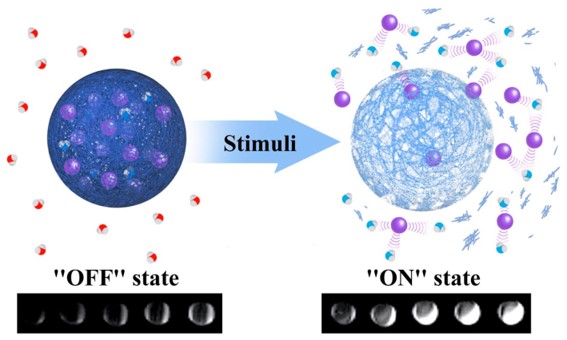
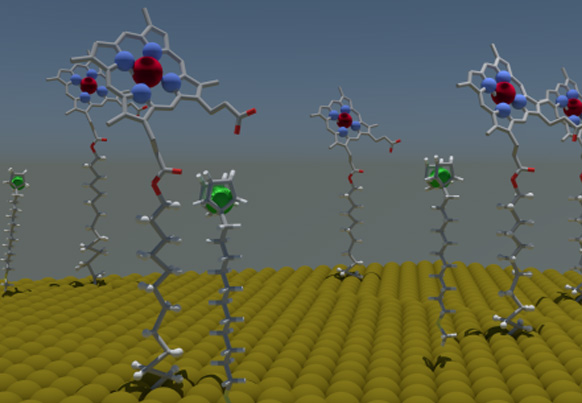
Ultrahigh magnetic resonance contrast switching with water gated polymer–silica nanoparticles
Chem. Commun., 2023,59, 6008-6011
Online Paper
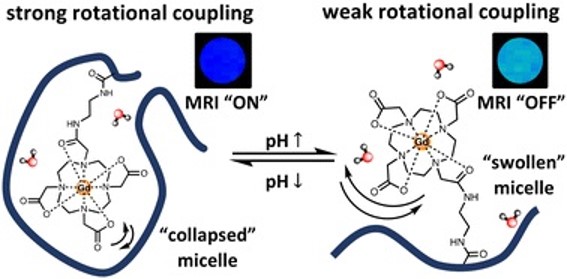
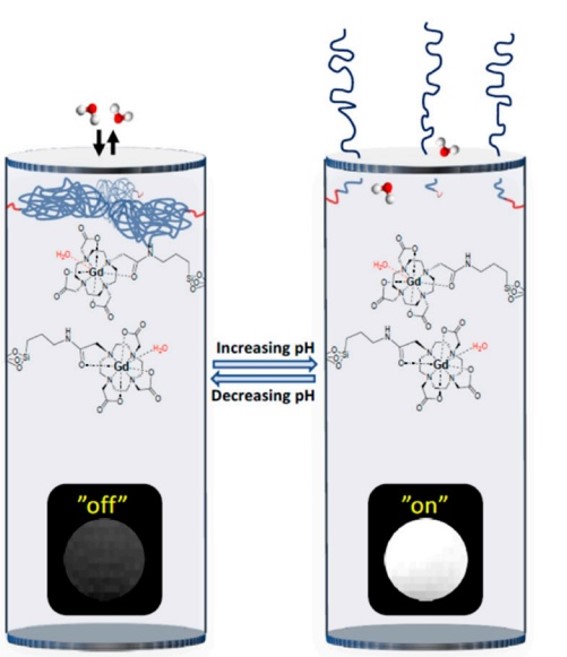
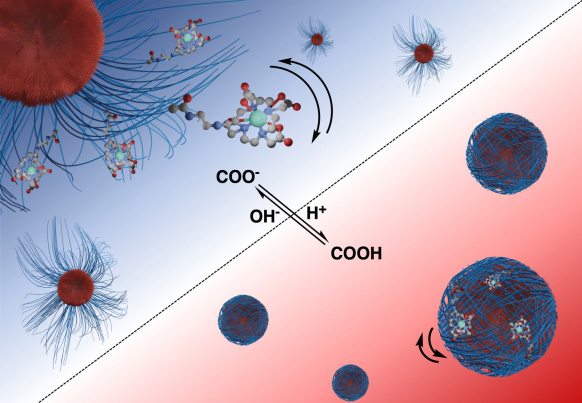
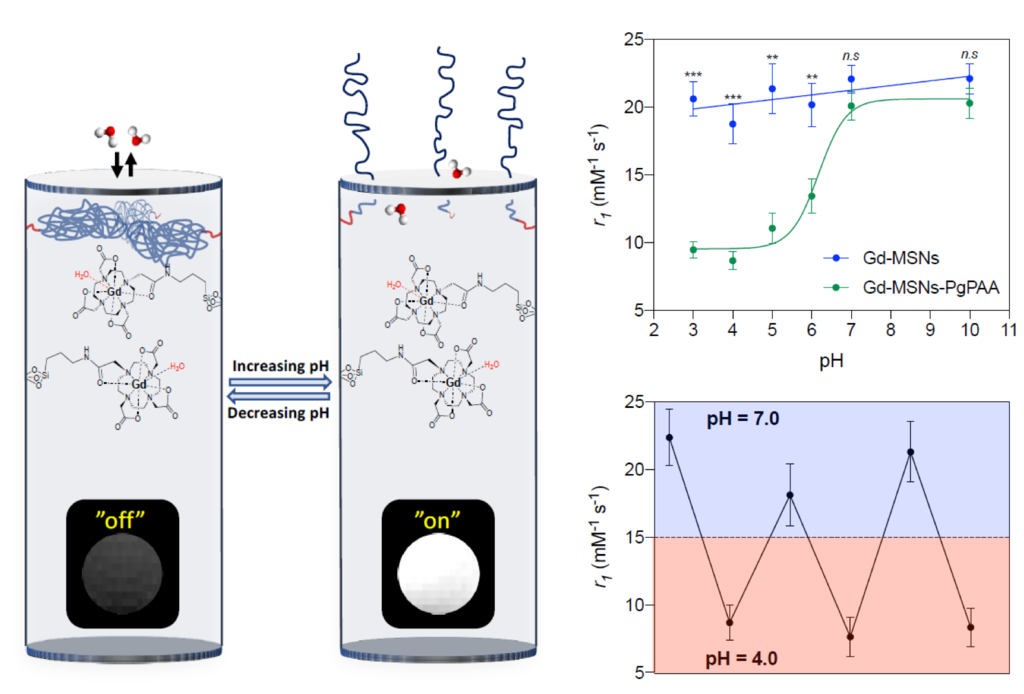
Reversible pH-responsive MRI contrast with paramagnetic polymer micelles
Chem. Commun., 2023,59, 1605-1608
Online Paper
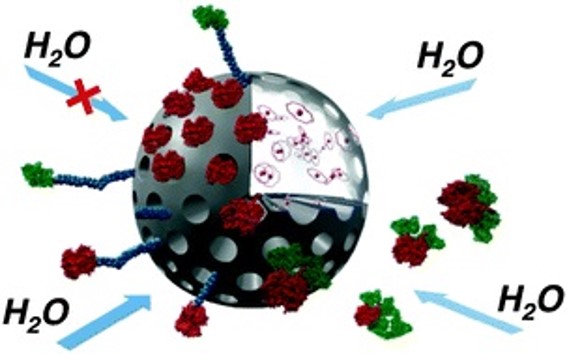
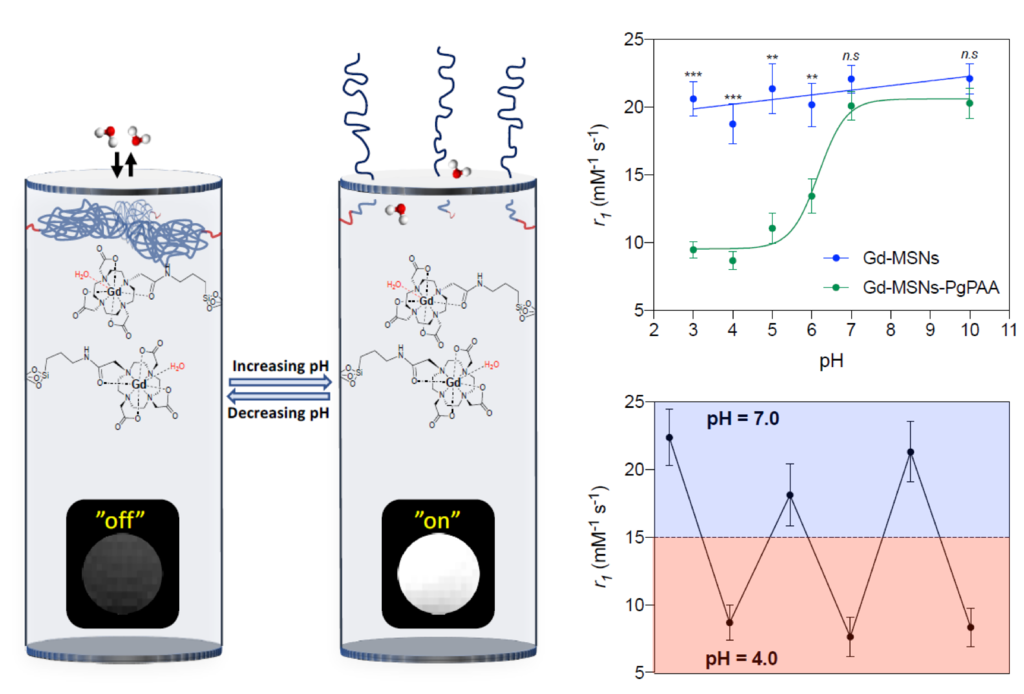
High signal contrast gating with biomodified Gd doped mesoporous nanoparticles
Chem. Commun., 2013,49, 60-62
Online Paper
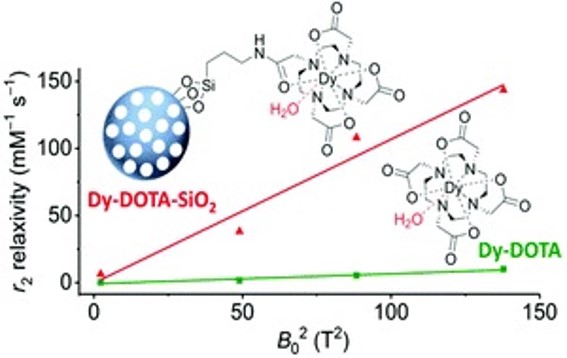
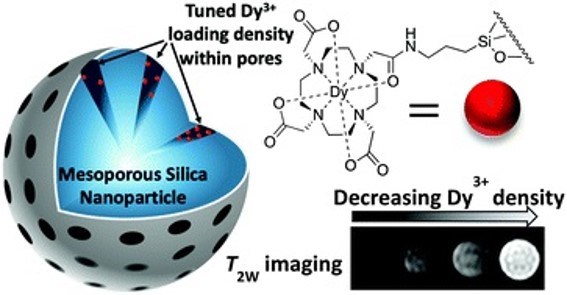
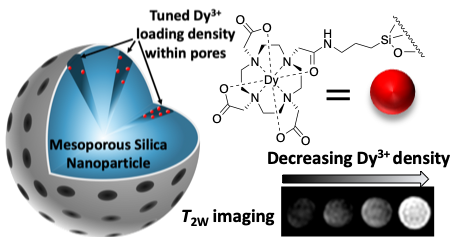
Dy-DOTA integrated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as promising ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents
Nanoscale, 2018,10, 21041-21045
Online Paper
Promoting high T2 contrast in Dy-doped MSNs through Curie effects
J.Mater. Chem. B, 2022, 10, 302
Online Paper
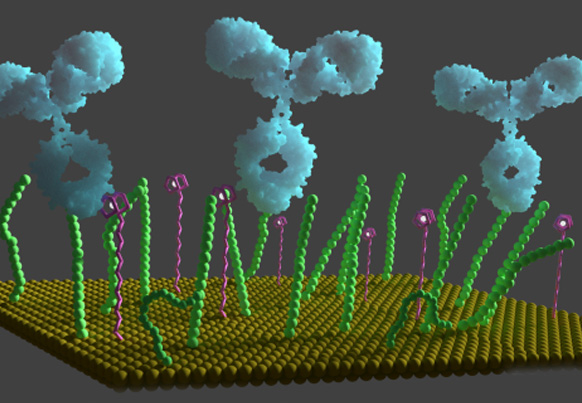
Water gated contrast switching with polymer–silica hybrid nanoparticles
Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 8540;
Online Paper
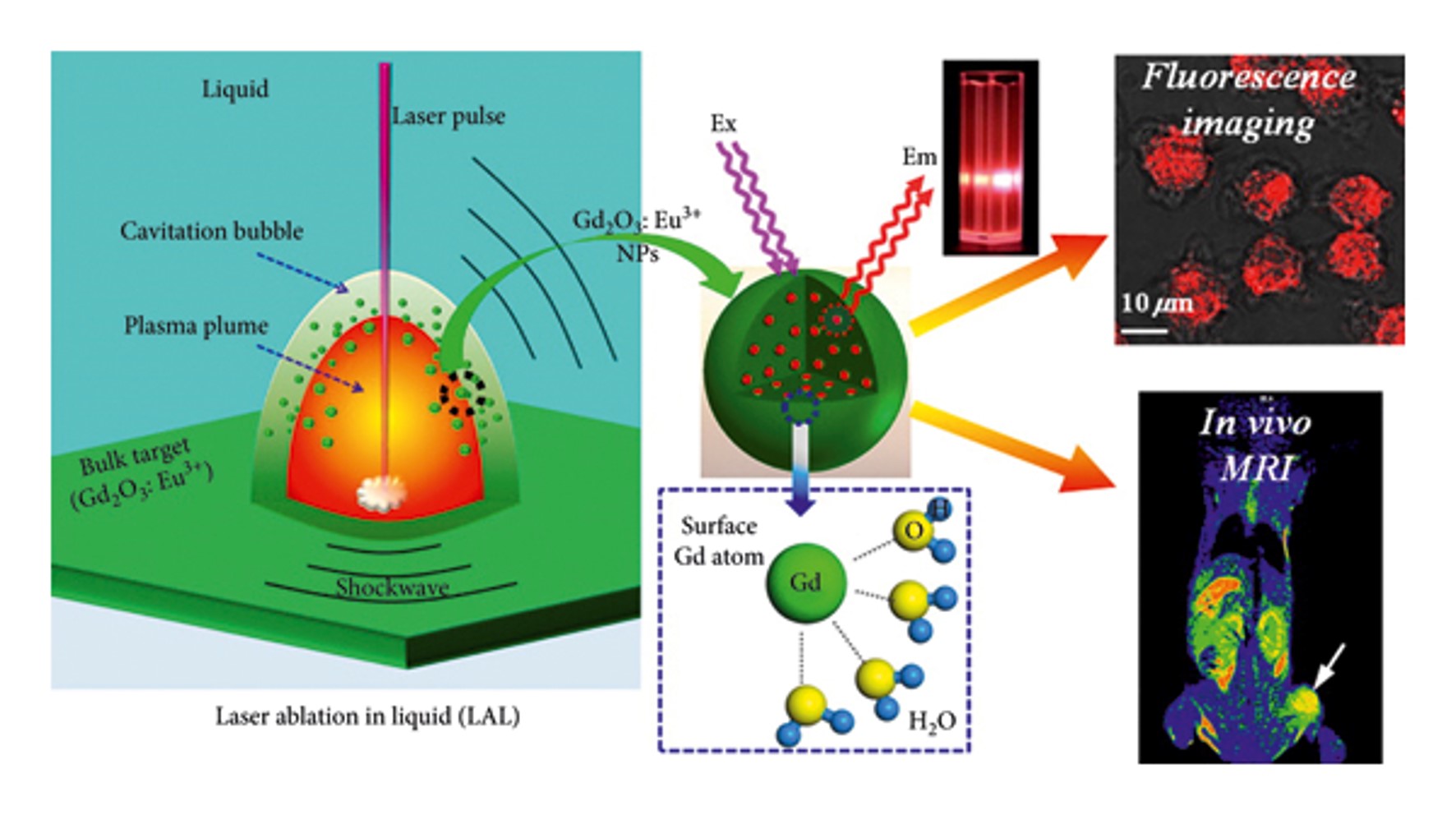
Nanoparticle-Based Paramagnetic Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Contrast Media Mol Imaging, 2019, 2019:1845637;
Online Paper
Magnetic Nanoparticles Supporting Bio-responsive T1/T2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Materials 2019, 12(24), 4096;
Online Paper